Spring Boot: REST controller Test example
updated 02.2022
In my Spring Boot - Angular showcase you can find some examples of REST controller tests.
The @RestController used for the example is the following:
@RestController
// we allow cors requests from our frontend environment
// note the curly braces that create an array of strings ... required by the annotation
@CrossOrigin(origins = {"${app.dev.frontend.local"})
public class HelloController {
// simple GET response for our example purpose, we return a JSON structure
@RequestMapping(value = "/message", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public Map<String, String> index() {
return Collections.singletonMap("message", "Greetings from Spring Boot!");
}
}
Test the controller using an embedded server (integration tests)
With this approach, Spring starts an embedded server to test your REST service.
To create these tests you have to add a dependency to :
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
In your test, you have to define a webEnvironment, in our case we create an environment with a random port number.
Defining the webEnvironment we can wire the TestRestTemplate that allows us to execute REST requests.
TestRestTemplate is fault-tolerant and can be used with Basic authentication headers. It doesn't extend RestTemplateif you encounter issues during r tests you should maybe try RestTemplate.
/**
* The goal of this class is to show how the Embedded Server is used to test the REST service
*/
// SpringBootTest launch an instance of our application for tests purposes
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class HelloControllerEmbeddedServerTest {
@Autowired
private HelloController helloController;
// inject the runtime port, it requires the webEnvironment
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
// we use TestRestTemplate, it's an alternative to RestTemplate specific for tests
// to use this template a webEnvironment is mandatory
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate restTemplate;
@Test
void index() {
// we test that our controller is not null
Assertions.assertThat(helloController).isNotNull();
}
@Test
void indexResultTest() {
Assertions.assertThat(restTemplate
.getForObject("http://localhost:" + port + "/message", String.class)).contains("from Spring Boot");
}
}
When you run the test you can notice in your console that Spring Boot runs a Tomcat Server.
INFO 4230 --- [main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat initialized with port(s): 0 (http)
INFO 4230 --- [main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat]
INFO 4230 --- [main] org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet engine: [Apache Tomcat/9.0.43]
INFO 4230 --- [main] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext
INFO 4230 --- [main] w.s.c.ServletWebServerApplicationContext : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 1761 ms
If you are trying to test GET methods with payload, this method could give you headaches.
RestTemplateTest doesn't like to add payloads to the GET request and you will receive an error response, you can read more in my post about the Spring Boot GET Test limitation.
MockMvc, testing without an embedded server
The previous controller could be tested with @MockMvc, this allows us to have tested the RestController without the overhead of a server (pushing us in the integration tests domain).
/**
* The goal of this class is to test the controller using a MockMvc object without an embedded server
*/
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc // we mock the http request and we don't need a server
public class HelloControllerMockMvcTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc; // injected with @AutoConfigureMockMvc
@Test
public void shouldReturnOurText() throws Exception {
this.mockMvc
.perform(get("/message")) // perform a request that can be chained
.andDo(print()) // we log the result
.andExpect(content().string(containsString(" from Spring"))); // we check that the Body of the answer contains our expectation
}
}
In this case Spring initializes a test Servlet without embedding a full server, from the console:
INFO 4589 --- [main] o.s.s.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor : Initializing ExecutorService 'applicationTaskExecutor'
INFO 4589 --- [main] o.s.b.a.w.s.WelcomePageHandlerMapping : Adding welcome page: class path resource [static/index.html]
INFO 4589 --- [main] o.s.b.t.m.w.SpringBootMockServletContext : Initializing Spring TestDispatcherServlet ''
INFO 4589 --- [main] o.s.t.web.servlet.TestDispatcherServlet : Initializing Servlet ''
INFO 4589 --- [main] o.s.t.web.servlet.TestDispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 0 ms
With the .andDo(print()) instruction many details are printed in the console (extract):
...
ModelAndView:
View name = null
View = null
Model = null
FlashMap:
Attributes = null
MockHttpServletResponse:
Status = 200
Error message = null
Headers = [Vary:"Origin", "Access-Control-Request-Method", "Access-Control-Request-Headers", Content-Type:"application/json"]
Content type = application/json
Body = {"message":"Greetings from Spring Boot!"}
...
(Old) Deep dive: @WebMvcTest, how it works
The annotation @WebMvcTest configure only the components that usually interest the web development.

As shown in the image @Service and @Repositoryare not configured.
When we call the @Service from the @Controller we return the mocked object.
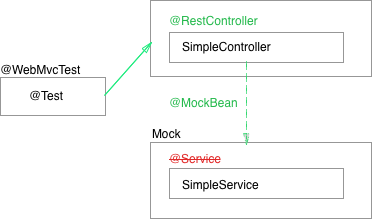
Controller example
This is a very simple controller that calls a service and returns a custom object containing a text value:
@RestController
public class SimpleController {
private SimpleService simpleService;
public SimpleController(SimpleService simpleService) {
this.simpleService = simpleService;
}
@GetMapping(value = "/simple",produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public ResponseEntity<StringJsonObject> simpleResult() {
return ResponseEntity.ok(simpleService.getText());
}
}
Here the service code:
@Service
public class SimpleServiceImpl implements SimpleService{
@Override
public StringJsonObject getText(){
return new StringJsonObject("Cool!");
}
}
The returned object:
public class StringJsonObject {
private String content;
public StringJsonObject(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
}
The test with comments
Here the code used to test the controller:
// SpringRunner is an alias of SpringJUnit4ClassRunner
// it's a Spring extension of JUnit that handles the TestContext
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
// we test only the SimpleController
@WebMvcTest(SimpleController.class)
public class SimpleControllerTest {
// we inject the server side Spring MVC test support
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
// we mock the service, here we test only the controller
// @MockBean is a Spring annotation that depends on mockito framework
@MockBean
private SimpleService simpleServiceMocked;
@Test
public void simpleResult() throws Exception {
// this is the expected JSON answer
String responseBody = "{\"content\":\"Hello World from Spring!\"}";
// we set the result of the mocked service
given(simpleServiceMocked.getText())
.willReturn(new StringJsonObject("Hello World from Spring!"));
// the test is executed:
// perform: it executes the request and returns a ResultActions object
// accept: type of media accepted as response
// andExpect: ResultMatcher object that defines some expectations
this.mockMvc.perform(get("/simple")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(responseBody));
}
}
